This is an old revision of the document!
Table of Contents
NeuroElf - RFX (single-level) mediation
Motivation
Contrast images assess the likelihood of observing an average brain response (across subjects) compared to its standard error under the Null-hypothesis (of no or no differential effect), and correlations assess the likelihood of observing as little residual with a predicted linear increase in those responses linked to a covariate (regressor) under the Null-hypothesis of no effect of the covariate. While this is already highly informative, it does not necessarily answer these questions:
- is the brain area in which an observed effect is assumed to be real necessary for the processing of the information?
- what consequences arise from the processes in the brain area of interest?
While even Mediation analysis cannot give definite answers to these questions, it clearly gets much closer to providing evidence for an affirmative answer to the first question and potentially also hypotheses for the second question. (Other methods trying to answer those questions include, for instance, TMS/rTMS which briefly or prolonged disrupt neural pathways, thus compromising the processing, hopefully leading to differential outcome/behavior).
Requirements
As with other functions from the Analysis menu, Mediation analysis has a few requirements:
- a RFX-GLM must be loaded
- the GLM must have contrasts configured
- the GLM must have covariates configured, which can be either
- behavioral or otherwise subject-specific and brain-data unrelated covariates (IQ, memory capacity, questionnaire data)
- voxel-based or cluster-averaged extracts of beta or contrast maps
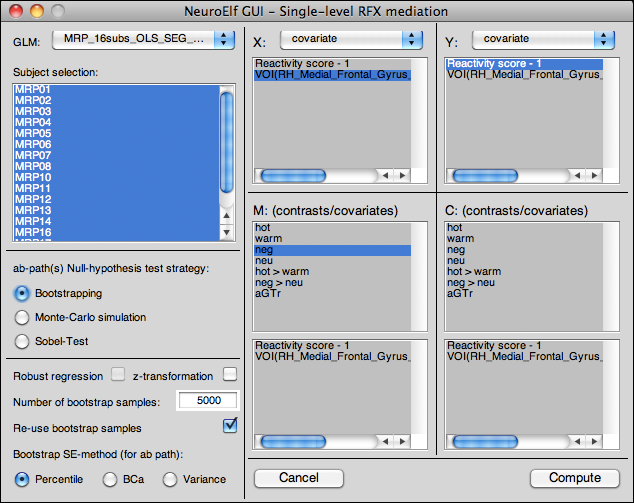
GUI layout
The RFX mediation analysis UI is available via the Single-level RFX mediation entry from the Analysis menu. When called, the following dialog pops up: